
What You Need to Know About Micro-Autoradiography (mARG) Distribution Studies
- In Vivo & Radiolabeling
- December 19, 2019
- Jolanta Golec, Madison Esely-Kohlman
In vivo determination of drug localization in tissue can be uniquely informative to drug developers investigating distribution within the context of the ADME/pharmacokinetic profile of their drug compounds. Micro-autoradiography can demonstrate sites of accumulation of a drug and drug-related material, which can be used as supplemental data for evaluation of parameters such as toxicity, efficacy, drug penetration, or differential metabolite distribution.
Micro-autoradiography histology techniques utilize photographic detection media (Nuclear Emulsion) to spatially locate drug-derived radioactivity at the cellular level in organ and tissue samples. Therefore, it provides opportunity for a more detailed examination than QWBA because microscopic radioactivity distribution can be analyzed in target tissues.
Our approach to radiolabeled ADME in drug discovery and development
Our partner, the Drug Development Solutions Center in Tokai, Japan, has been offering micro-autoradiography (mARG) as a tissue distribution analytical method for more than 30 years, accumulating a wealth of experience in histology, drug deposition, and radioactivity. Like other radiolabeled ADME services, mARG requires a high degree of technical skill and our team at DDSC has extensive experience and training to provide you consistent sections, precise qualitative analysis, and educated interpretation of results.
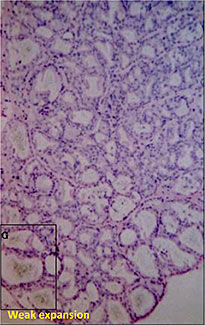
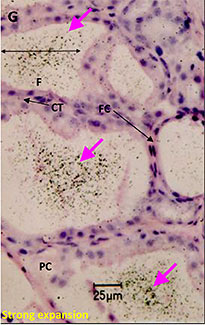
Microautoradiography showing accumulation in the follicles of rat thyroid gland after repeated administration
Used as supplemental data for evaluation of toxicity
F:Follicles
CT:Connective tissue
FC:Follicular cells
PC:Parafollicular cells
mARG study highlights
- Specialized thaw mount method
- AAALAC-accredited facility; 150,000 ft2 campus featuring animal care units
- Consistent 5 μm slices exposed to nuclear emulsion for radioactive compound visualization
- HE stained slides for reference
- 4-week turnaround time for data/report

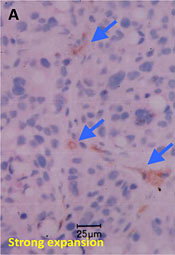
Method
Fresh tissue or organ samples are snap-frozen, cryosectioned at 5 μm thickness, and exposed to nuclear emulsion that has been put on glass microscope slide for 1 – 4 weeks. After the exposure, the slides are developed, stained, and analyzed using a Leica LEITZ LMR light microscope to visually distinguish the localization of the radioactive drug derivative in individual cells.
Additional quantitative comparison
Consecutive 5 μm mARG horizontal skin slices may be considered together to better understand drug penetration in terms of depth. The figure below shows our capabilities to create a histogram from data from multiple skin slices, at 20 um intervals, to quantify radioactivity at sequential depths.
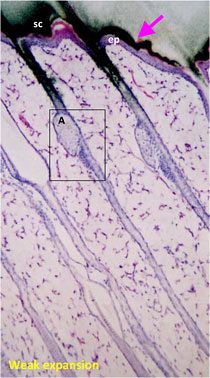
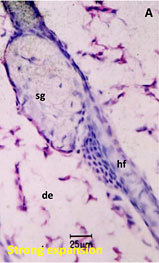
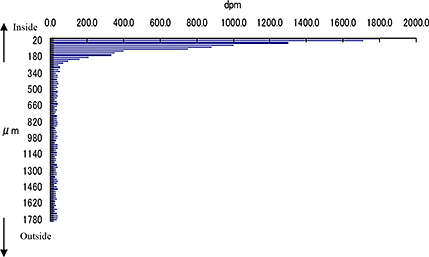
Drug penetration in skin sections with histogram to inform quantitative distribution data
sg:Sebaceous glands
de:Dermis
ep:Epidermis
sc:Stratum corneum
hf:Hair follicle
Through our partners, XenoTech offers the following options:
Tissue capabilities
- Adrenal Gland
- Brain
- Lung
- Liver
- Intestine
- Kidney
- Muscle
- Pancreas
- Retina
- Skin
- Spleen
- Thyroid Gland
- Tumor
- Other tissue types maybe possible upon request
Radionuclides
- 14C
- 3H
- 125I
- 33P
- 35S
- 51Cr
- 111In
- 55Fe
- 59Fe
- 65Zn
- 75Se
- 90Y
- 153Gd
Animal species
- Rat
- Mouse
- Rabbit
- Dog
- Monkey
- Miniature Pig
- Animal models of human disease
- Knock Out animals
- Chimeric Mice with highly humanized liver
- Others may be available upon request
Contact Us with Questions, Feedback or Requests
Learn more about:
[1] M3 (R2) https://www.fda.gov/media/71542/download
[2] 21CFR312.23 https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/cfcfr/CFRSearch.cfm?FR=361.1
[3] https://www.bioanalysis-zone.com/2018/03/09/quantitative-whole-body-autoradiography-qwba-imaging-mass-spectrometry-ims-can-ims-replace-qwba-support-regulated-drug-discovery-development/
About the Authors
Related Posts
DDSC In Vivo ADME Expertise Providing Cost Savings
In Vivo ADME: What You Need and Why You Need It
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Stay up to date with our news, events and research

Do you have a question or a request for upcoming blog content?
We love to get your feedback
