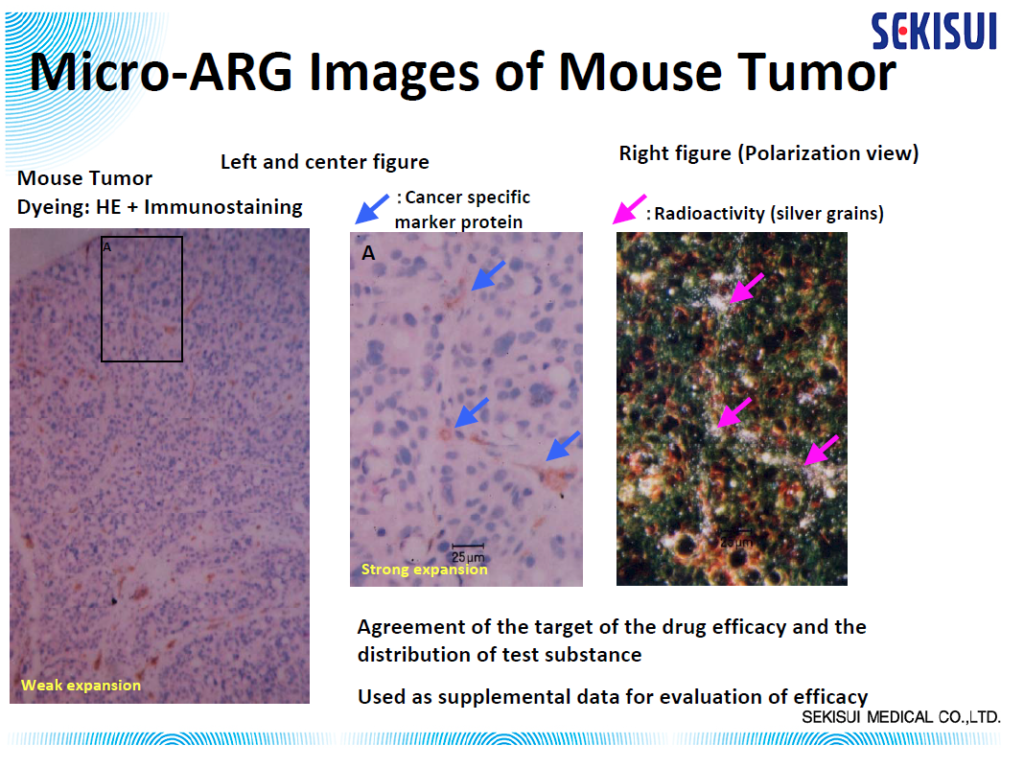
In vivo determination of drug localization in tissue can be uniquely informative to drug developers investigating distribution within the context of the ADME/pharmacokinetic profile of their drug compounds. Micro-autoradiography can demonstrate sites of accumulation of a drug and drug-related material, which could be used as supplemental data for evaluation of parameters such as toxicity, efficacy, drug penetration, or differential metabolite distribution.

Micro-Autoradiography (mARG) Tissue Distribution Technique
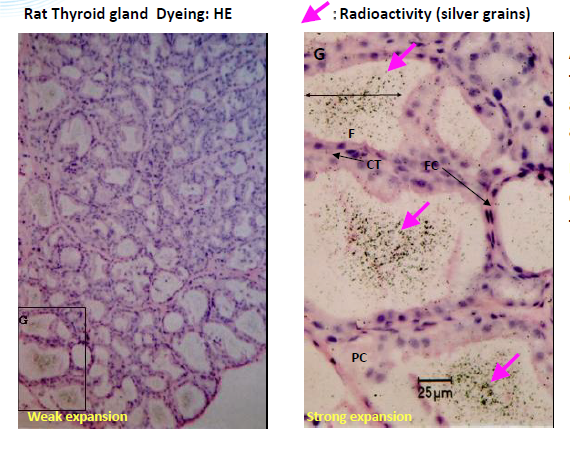
Micro-autoradiography histology techniques utilize photographic detection media (nuclear emulsion) to spatially locate drug-derived radioactivity at the cellular level in organ and tissue samples. Therefore, it provides an opportunity for a more detailed examination than Quantitative Whole Body Autoradiography because microscopic radioactivity distribution can be analyzed in target tissues.
Our Approach to Radiolabeled ADME in Drug Discovery and Development
Our partners in Japan, the SEKISUI Drug Development Solutions Center, has been offering micro-autoradiography (mARG) as a tissue distribution analytical method for more than 30 years, accumulating a wealth of experience in histology, drug deposition, and radioactivity. Like other radiolabeled ADME services, mARG requires a high degree of technical skill and our team at DDSC has extensive experience and training to provide you consistent sections, precise qualitative analysis, and educated interpretation of results.
mARG Study Highlights
- Specialized thaw mount method
- AAALAC International-accredited facility; 150,000 ft2 campus featuring animal care units
- Consistent 5 μm slices exposed to nuclear emulsion for radioactive compound visualization
- HE stained slides for reference
- 4-week turnaround time for data/report
Micro-autoradiography Methods
Fresh tissue or organ samples are snap-frozen, cryosectioned at 5 μm thickness, and exposed to a nuclear emulsion that has been put on a glass microscope slide for 1–4 weeks. After the exposure, the slides are developed, stained, and analyzed using a Leica LEITZ LMR light microscope to visually distinguish the localization of the radioactive drug derivative in individual cells.
Additional Capabilities: Quantitative Comparison
Consecutive 5 μm mARG horizontal skin slices may be considered together to better understand drug penetration in terms of depth. The figure below shows our capabilities to create a histogram from data from multiple skin slices, at 20 μm intervals, to quantify radioactivity at sequential depths.

| Tissue Capabilities | Radionuclides | Animal Species |
|---|---|---|
|
Adrenal Gland |
14C |
Rat Mouse Rabbit Dog Monkey Miniature Pig Animal models of human disease Knock Out Animals Chimeric Mice with highly humanized liver Others may be available upon request |
Related Service: QWBA
Quantitative Whole Body Autoradiography (QWBA) is another in vivo autoradiography study method in which a rat (or in some cases mouse) is dosed with radiolabeled test article and at successive time points radioactivity is measured in cross-sectioned slides of the whole animal to show distribution over time and achieve critical input data for dosimetry calculations for first in-human (FIH) radiolabeled mass balance studies.

